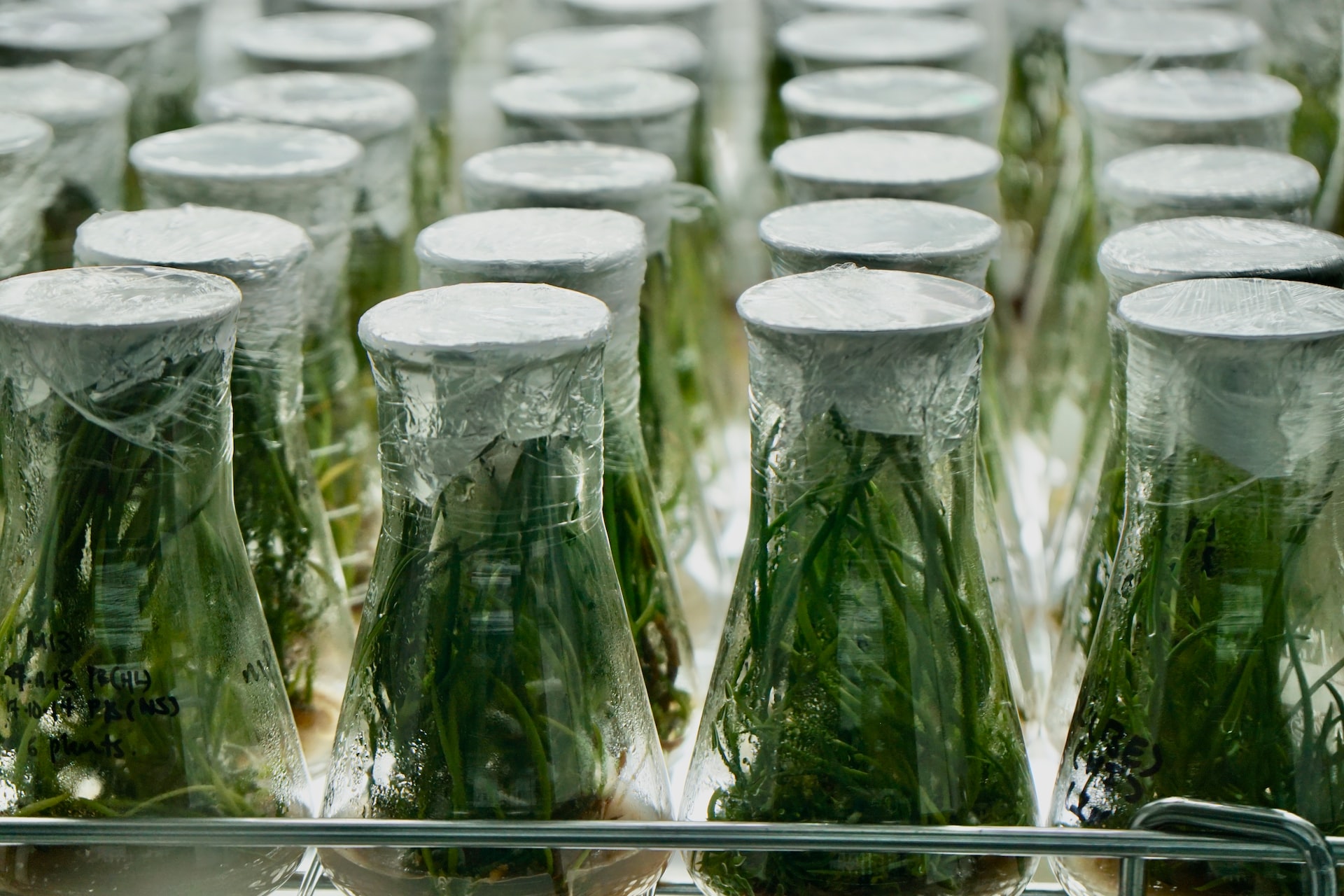
Tissue Culture
Plant tissue culture is a great way to propagate plants and produce new plants from cuttings. In this beginner's guide, we will discuss the methods and nutrient media used in plant tissue culture. Plant tissue culture is the process of culturing plant cells and tissues in vitro for the purpose of producing new plants. This process can be used to produce plants that are genetically identical to the original plant, or to produce plants with new or desirable traits. Plant tissue culture is a valuable tool for plant breeding and for the study of plant physiology and molecular biology.

Methods of plant tissue culture
There are many methods of plant tissue culture that can be used to propagate plants. One of the most popular methods is the use of agar media. Agar media is a seaweed extract that is used to provide a nutrient-rich environment for plant cells. It is often used to culture plant cells in a laboratory setting.
Nutrient media
The types of nutrient media used in a bioreactor are determined by the microorganisms being cultured and the desired product. The most common components of nutrient media are water, minerals, and organic compounds. The concentration and composition of nutrients in media can be manipulated to favor the growth of certain microorganisms or to produce a desired product.
Totipotent cells and meristem culture
Totipotent cells and meristem culture are both important tools for plant breeding and genetic modification. Totipotent cells are able to create a complete plant, while meristem culture can be used to propagate plants quickly and easily. By using these tools, plant breeders and geneticists can create new plants with desired traits more quickly and easily than ever before.
Pollen culture
Pollen culture is a process that is used to grow pollen in a laboratory setting. Pollen is a powdery substance that is produced by flowers and that is used to fertilize other flowers. Pollen culture can be used to produce pollen for research purposes or to create new varieties of plants.
Embryo culture
Embryo culture is the process of culturing embryos in vitro. This is typically done in a laboratory setting, and can be used for a variety of purposes, including fertility treatments, genetic research, and animal breeding. Embryo culture is a relatively new technology, and there are still some questions about its safety and efficacy. However, it has already shown great promise in helping to improve fertility rates and to advance medical research.
Nucellus and embryo culture
Nucellus and embryo culture are two important techniques used in the field of reproductive biology. Nucellus culture is the process of culturing the cells that make up the nucellus, while embryo culture is the process of culturing the cells that make up the embryo. These techniques are used to improve the efficiency of in vitro fertilization (IVF) and embryo transfer (ET) procedures.
Applications of plant tissue culture
Tissue culture is a valuable tool for the plant scientist, and has many applications, including the following:
- 1. Plant tissue culture can be used to produce virus-free plants. This is important for crops that are susceptible to viral diseases.
- 2. Tissue culture can be used to produce plants with novel traits. This can be used to create new varieties of crops or to improve the yield or quality of crops.
- 3. Tissue culture can be used to produce plants that are resistant to disease or pests. This can help to improve the sustainability of crops.
- 4. Tissue culture can be used to produce plants that are tolerant to stress. This can help to improve the yield or quality of crops.
- 5. Tissue culture can be used to produce plants that are genetically modified. This can be used to create new varieties of crops or to improve the yield or quality of crops.